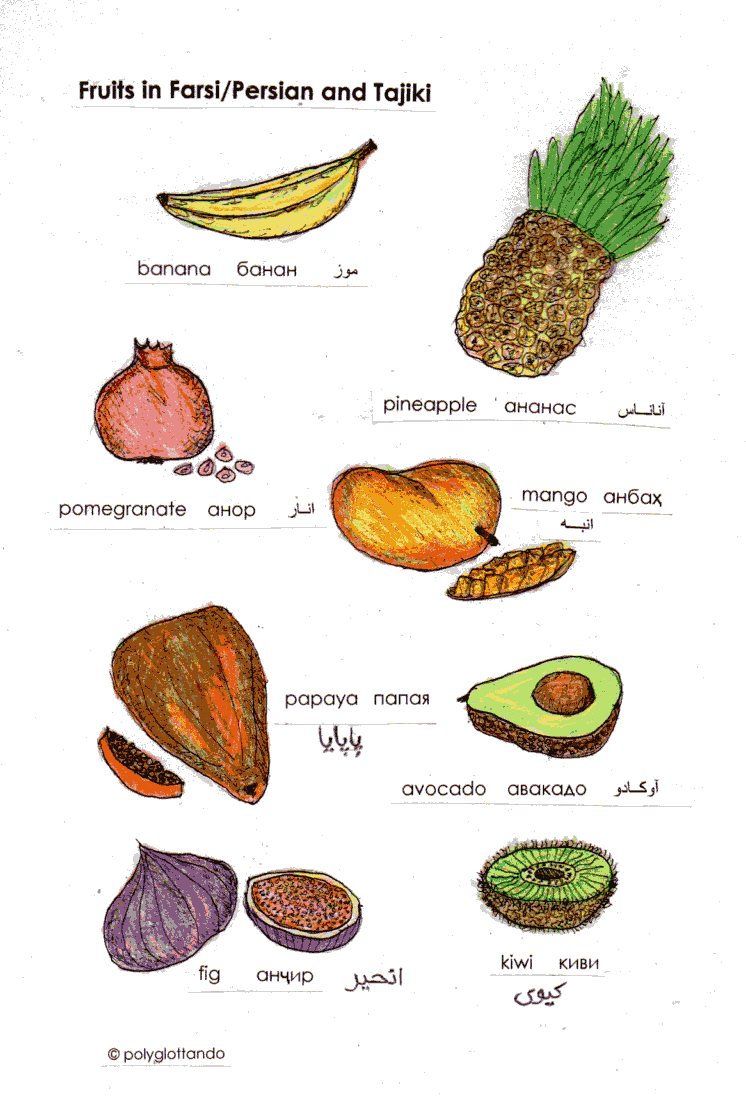
Author: Gustav @ Flickr, via Wikipedia Commons
Today’s blog post continues our culture series about interesting customs from all over the world and takes us to Bulgaria again and to Baba Marta Day with its Martenitsi which is celebrated on 1 March.
According to Bulgarian folklore Баба Марта, Baba Marta or ‘Grandma March’, is a grumpy old lady who is grudging at her two brothers and whose mood is said to determine the weather, so the sun only shines when she is smiling. There are different versions of the Baba Marta tale. One of them relates that Baba Marta is doing her spring cleaning on this day: While she is shaking her feather-filled blanket, all the feathers come out of it and fall down to Earth as the last snow of the year. This version of the tale has parallels to the German folktale of Mother Hulda (‘Frau Holle‘).
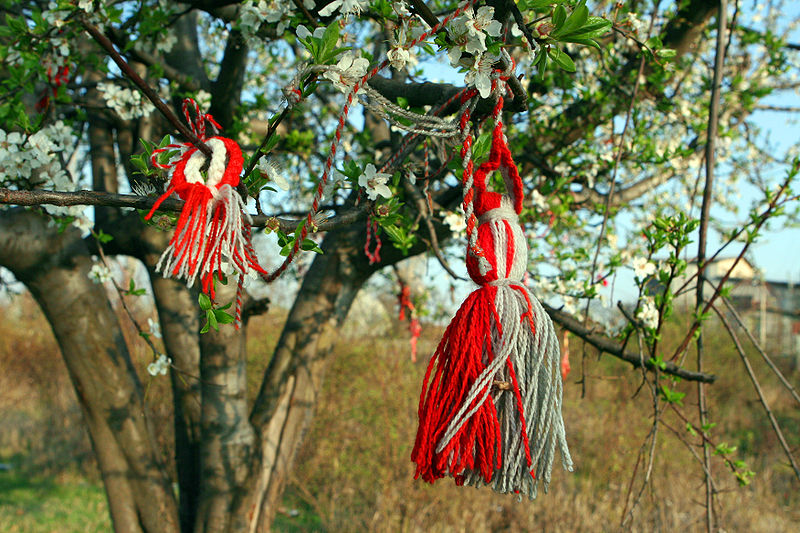
Bulgarians celebrate 1 March by observing the centuries-old custom of exchanging Мартеници Martenitsi in order to ask Baba Marta for mercy, in the hope that winter will pass faster and spring come sooner.
A Martenitsa (Bulgarian: мартеница, Macedonian: мартинка) is a small woollen ornament, made of red and white interwoven yarn, which usually takes the shape of two dolls, a male and a female. These are called Пижо и Пенда (Pizho and Penda): The male Pizho is predominantly white, while the female Penda is predominantly red and wears a skirt. Sometimes, the Martenitsi just take the shape of a red-and-white interwoven ribbon. The Martenitsi are good luck charms symbolizing health and happiness for the year and are said to protect against evil spirits. They are also a reminder that spring is near.

Author: Petko Yotov, via Wikipedia Commons Pizho and Penda
Traditionally, they are given away as gifts to friends and family, i.e. not bought for oneself, and are worn around the wrist or attached to one’s clothes for a certain period of time, usually until the first signs of spring appear, e.g. the sightings of a swallow, a stork or a crane, or blossoming trees. Then the Мартеници (Martenitsi) are removed. In the small mountain villages, people also decorate their homes and domestic animals with the Martenitsi. There are different rituals associated with the removal of the Martenitsi, which are different in every region. Some people tie their Martenitsi on a branch of a fruit tree, thereby also giving the tree the good luck that comes from the charm.Other people lay their Martenitsi under a rock, in the belief that the insect that will be closest to the charm the next morning will determine the owner’s health and luck for the rest of the year: If the insect is a worm червей or a larva ларви, the coming year will be full of success and health; if it is an ant мравка, the person will have to work hard to be successful; however, if the insect is a spider паяк, the person may not enjoy success or good health in the year to come.
The red and white colours of the charms are also associated with a colour symbolism: white бял symbolizes purity and red червен life and passion. At its origin, the custom therefore symbolized the cycles of life and death, good and evil, and of sorrow and happiness in human existence. White originally also stood for Man and the power of the sun, and under Christian influence came to stand for virginity and integrity and was the colour of Christ. Red stood for Woman and health, being a symbol of blood, conception and birth. The colours of the Martenitsi also symbolize Mother Nature: white symbolizes the purity associated with melting snow, while red stands for the colour of the setting sun.
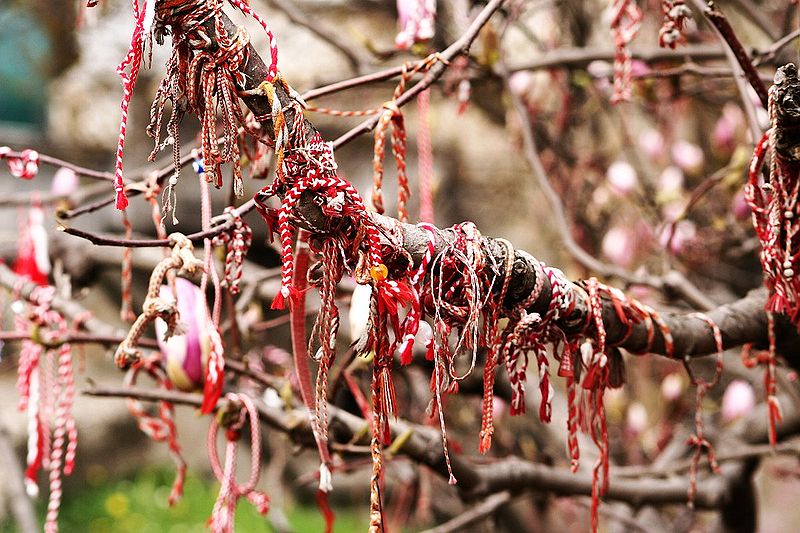

Author: Danielgrad via Wikipedia Commons Magnolia full of tied Martenitsa, in Veliko Tarnovo (Велико Търново)
The custom of exchanging Martenitsi is thought to have been inspired by an incident in the life of Bulgaria’s first Khan Аспарух (Asparuh), who sent a white string to his wife to let her know that he survived a battle.
A similar tradition also exists in the Republic of Macedonia, as well as in Albania, Northern Greece, Romania and Moldova. Its origin derives from ancient pagan agricultural cults of nature common to the Balkan Peninsula. The specific ritual of tying red-and-white woolen strings suggests Thracian, Hellenic or even Roman origins of the tradition.
Is there a similar tradition associated with spring in your country or region? Tell us about it in the comments! 🙂